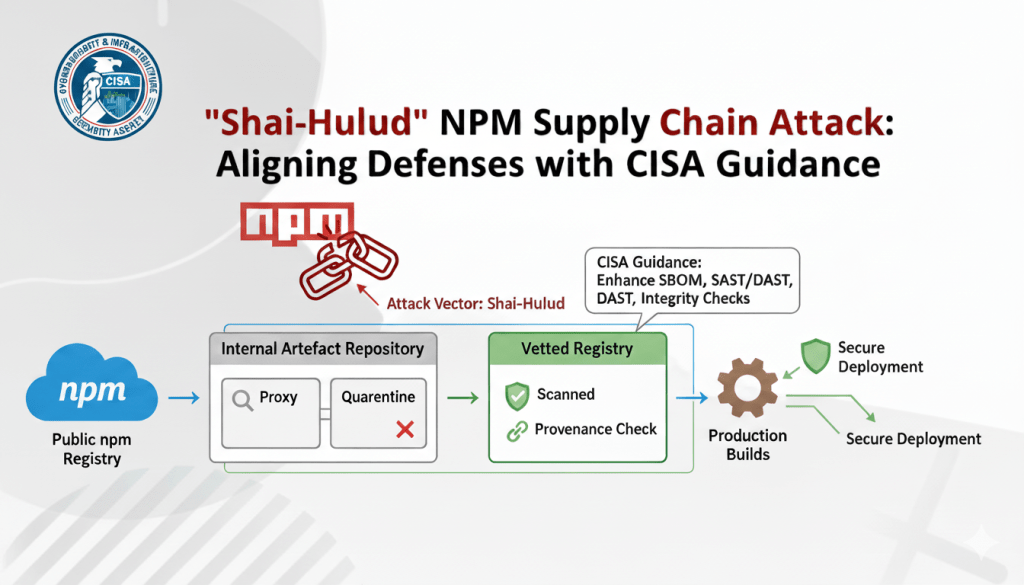
The npm ecosystem, powering millions of JavaScript projects, has just experienced one of the most disruptive supply chain attacks to date. The Shai-Hulud worm spread through compromised npm packages, stealing secrets and self-propagating across projects. Over 500 packages were impacted.
This post breaks down the incident, highlights CISA’s official recommendations, and introduces the curated registry model — a practical, long-term defense that every organization should adopt.
The Incident at a Glance
Attackers compromised developer accounts and published malicious package updates.
Injected code exfiltrated GitHub PATs, AWS, GCP, and Azure API keys.
Secrets were sent to attacker-controlled endpoints, some using webhook.site.
The worm spread automatically, publishing further poisoned packages from new victims.
Sources: CISA, GitHub Blog, Socket, Trend Micro, Palo Alto Unit42, Wiz, SecurityWeek.
Why It Matters
Scale: Over 500 compromised packages = thousands of downstream repos at risk.
Automation: The worm replicated faster than traditional malware campaigns.
Cloud impact: Stolen secrets provided access into critical infrastructure.
CISA’s Emergency Guidance
From CISA’s September 23, 2025 alert :
- Audit Dependencies: Review all direct and transitive npm dependencies (
package-lock.json). - Check Internal Repositories: Inspect cached artifacts for malicious versions.
- Pin Safe Versions: Roll back to trusted versions pre–Sept. 16, 2025.
- Rotate All Secrets: Reset developer PATs, API keys, and credentials.
- Mandate Phishing-Resistant MFA: FIDO2 keys or equivalent for GitHub/npm accounts.
- Harden GitHub: Audit webhooks, enforce branch protection, review OAuth apps.
- Block Malicious Domains: Prevent traffic to known exfil endpoints like
webhook.site. - Enable Security Features: Use GitHub secret scanning and Dependabot alerts.
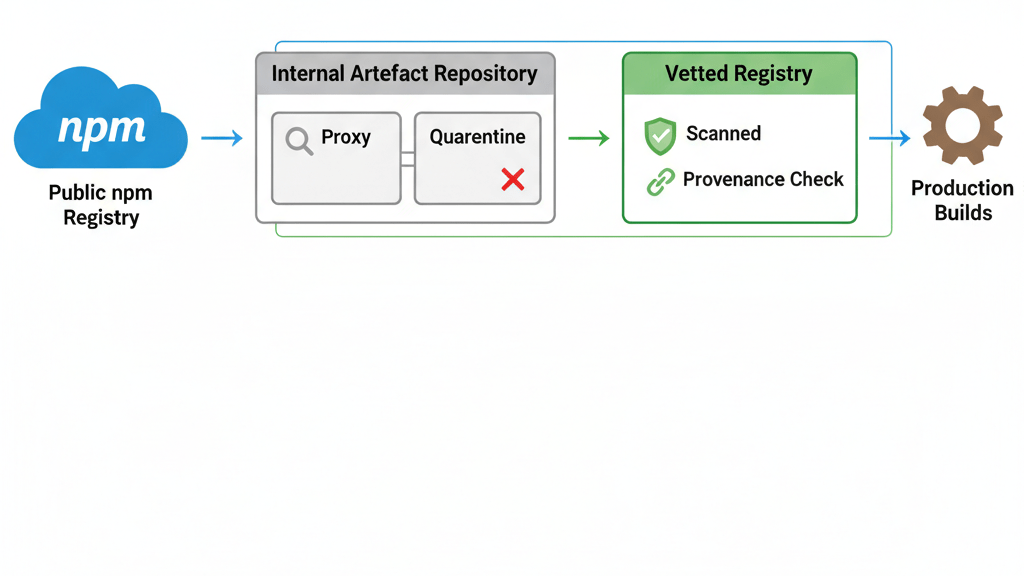
Beyond Emergency Response: The Curated Registry Model
CISA gives you the “what to do now.” But long-term resilience requires changing how dependencies enter your environment.
🔐 The Model
- Proxy npm through an internal artifact repository (e.g., Artifactory, Nexus, GitHub Packages).
- Quarantine first-time packages until reviewed and scanned.
- Automated scanning (malware, CVEs, secrets) before promotion.
- Enforce provenance (npm package attestations, SLSA levels).
- Promotion pipelines (
quarantine → vetted → approved → production). - Lock down consumers with
.npmrcand CI/CD enforcement.
Example
Sample Config: Enforcing Internal Registry
.npmrc
registry=https://artifactory.example.com/api/npm/npm-vetted/
//artifactory.example.com/api/npm/npm-vetted/:_authToken=${NPM_TOKEN}
always-auth=true
This forces developers and CI jobs to only consume packages from the internal vetted registry.
GitHub Security Hardening
Branch Protection (example policy):
- Require signed commits.
- Require 2 reviewers for PRs that update
package.jsonorpackage-lock.json. - Require status checks for dependency diff scans.
Secret Scanning Alerts:
- Enable GitHub Advanced Security → Secret scanning → Push protection.
Closing Thoughts
The Shai-Hulud worm is a wake-up call: supply chain attacks are no longer isolated incidents but systemic risks.
- Short-term: Follow CISA’s emergency steps — audit dependencies, rotate secrets, enforce MFA.
- Long-term: Build a curated registry pipeline — treat npm packages as untrusted until verified.
By combining immediate response with sustainable architecture, organizations can not only recover from Shai-Hulud but emerge stronger against the next wave of supply chain threats.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer
The information in this report is being provided “as is” for informational purposes only. I do not endorse any commercial entity, product, company, or service, including any entities, products, or services linked within this document. Any reference to specific commercial entities, products, processes, or services by service mark, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not constitute or imply endorsement, recommendation, or favouring by me.

Leave a comment